Because Dad Deserves More Than Socks
Please login to view the price
login
healthy heels

protected skin

hydrated skin

anti-aging

dna shield
Free item with The Dad Gift:

Silicone Heel Guards




SHIPPING
- Shipping Guarantee: Guiding you to healthy skin isn’t only about our products; it's also about getting them to you as swiftly as the science behind them. That's why Dermal Health offers a shipping guarantee you can rely on.
- Where We Ship From: Orders are dispatched from our facilities in Pretoria.
- Who We Ship With: We trust only well-known, popular, and dependable courier services with your packages.
- When You'll Get It: Expect confident skin soon! Shipping addresses in Pretoria and Johannesburg will enjoy delivery from same-day to 2 business days. Shipping addresses further from Pretoria may expect delivery within 1-4 business days, depending on the service you select during checkout. Your estimated delivery date will reflect during checkout so that you can mark your calendar.
- Tracking Your Order: Eager to start your DermExcel journey? We don't blame you! You'll receive a tracking number after you place your order so that you can follow your package.
For any shipping inquiries, our customer service team is ready to assist.
SECURE PAYMENT
Dermal Health Science 30-Day Confidence Guarantee: We are passionate about guiding you to healthy skin through medical science. We believe in the quality and effectiveness of our products so much that we offer a 30-Day Confidence Guarantee. If you're unsatisfied with your purchase, simply return it within 30 days for a full refund.
Healthy Skin Is Not Complicated and neither is our return policy. Please visit our detailed return policy or contact our friendly customer service team for more information.
Feel as confident in us as we want you to feel in your skin.
Celebrate Dad with a gift set that perfectly balances rugged sophistication and advanced self-care. This luxurious collection has been curated for the dad who deserves to feel pampered while embracing his everyday challenges. From skincare solutions to a premium leather accessory, this set offers everything he needs to feel rejuvenated and ready to conquer the day.
What’s Inside
Genuine Leather Key Ring
A refined essential for Dad. Crafted from durable genuine leather, the DermExcel Key Ring offers everyday practicality with a timeless, masculine edge. Its minimalist design and subtle branding make it a stylish piece he’ll use day after day.
Dermalytic
Give the gift of smooth, revitalized skin with Dermalytic—the clinically formulated solution for dry, rough, and calloused areas. Packed with 10% Glycolic acid, 10% Lactic acid, and 20% Urea, this powerful cream-ointment goes beyond basic hydration, exfoliating and softening skin for long-lasting results. Perfect for the dad who’s always on his feet, Dermalytic tackles the toughest skin, leaving it smooth, healthy, and more youthful. A hardworking product for a hardworking dad.
Silicone Heel Guards
Designed for dad’s ultimate comfort, these Silicone Heel Guards are made from high-quality medical-grade silicone to provide targeted relief for dry, cracked, or painful heels. Whether he’s on the go or at rest, these heel guards help seal in moisture and protect against friction and discomfort. Pair them with Dermalytic Cream for an overnight skin transformation, ensuring dad wakes up to smooth, hydrated feet, ready for whatever the day holds.
Dermdefence SPF 50
Dad’s daily essential for skin protection—Dermdefence SPF 50 is more than just sunscreen. This pioneering formula provides broad-spectrum protection against UVA, UVB, infrared rays, and blue light, keeping his skin safe from sun damage and external aggressors. Fragrance-free and non-comedogenic, it’s perfect for sensitive skin types or those with conditions like acne or rosacea. With its lightweight, non-greasy feel and easy application, Dermdefence ensures he’s protected and looks great all day—whether outdoors or under a suit.
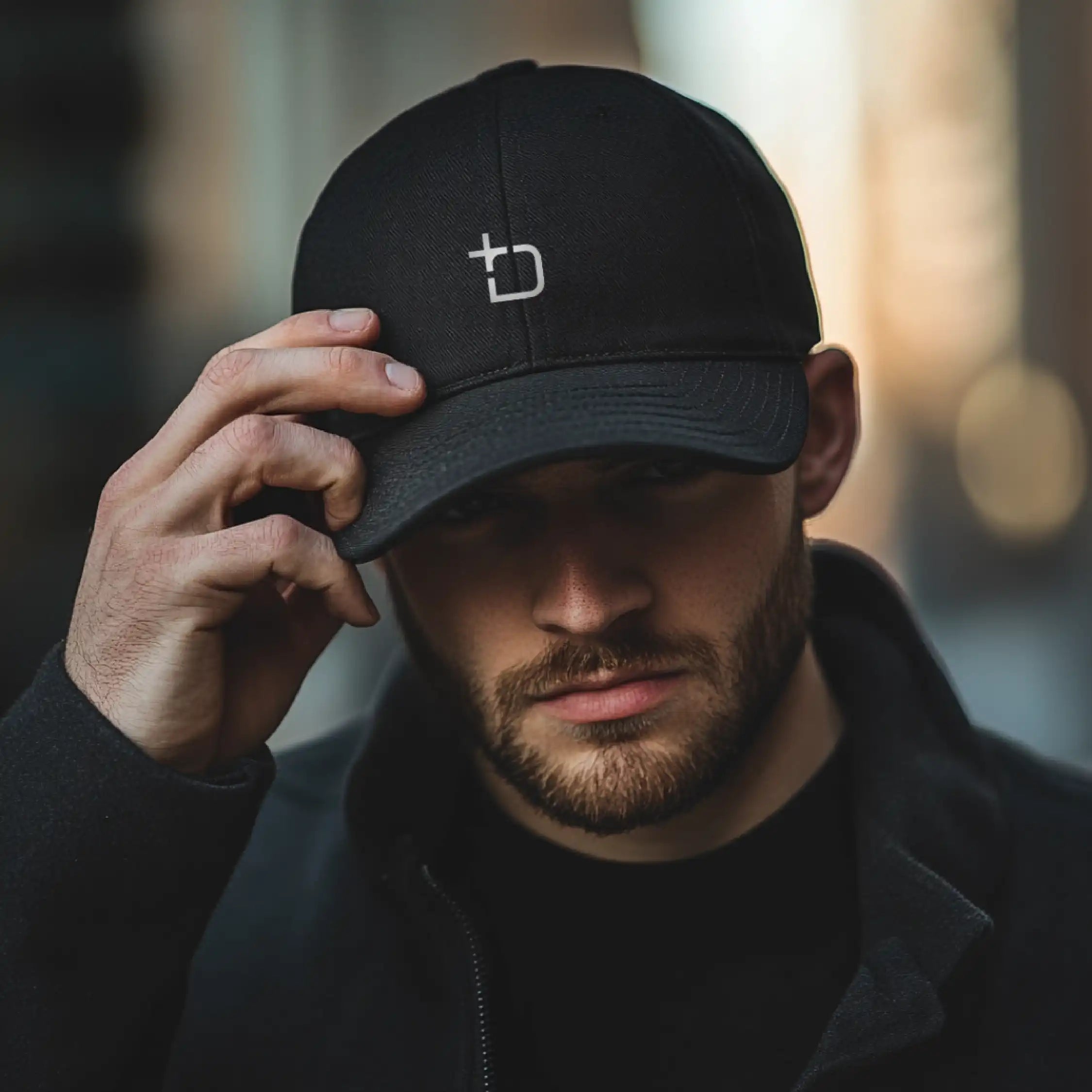
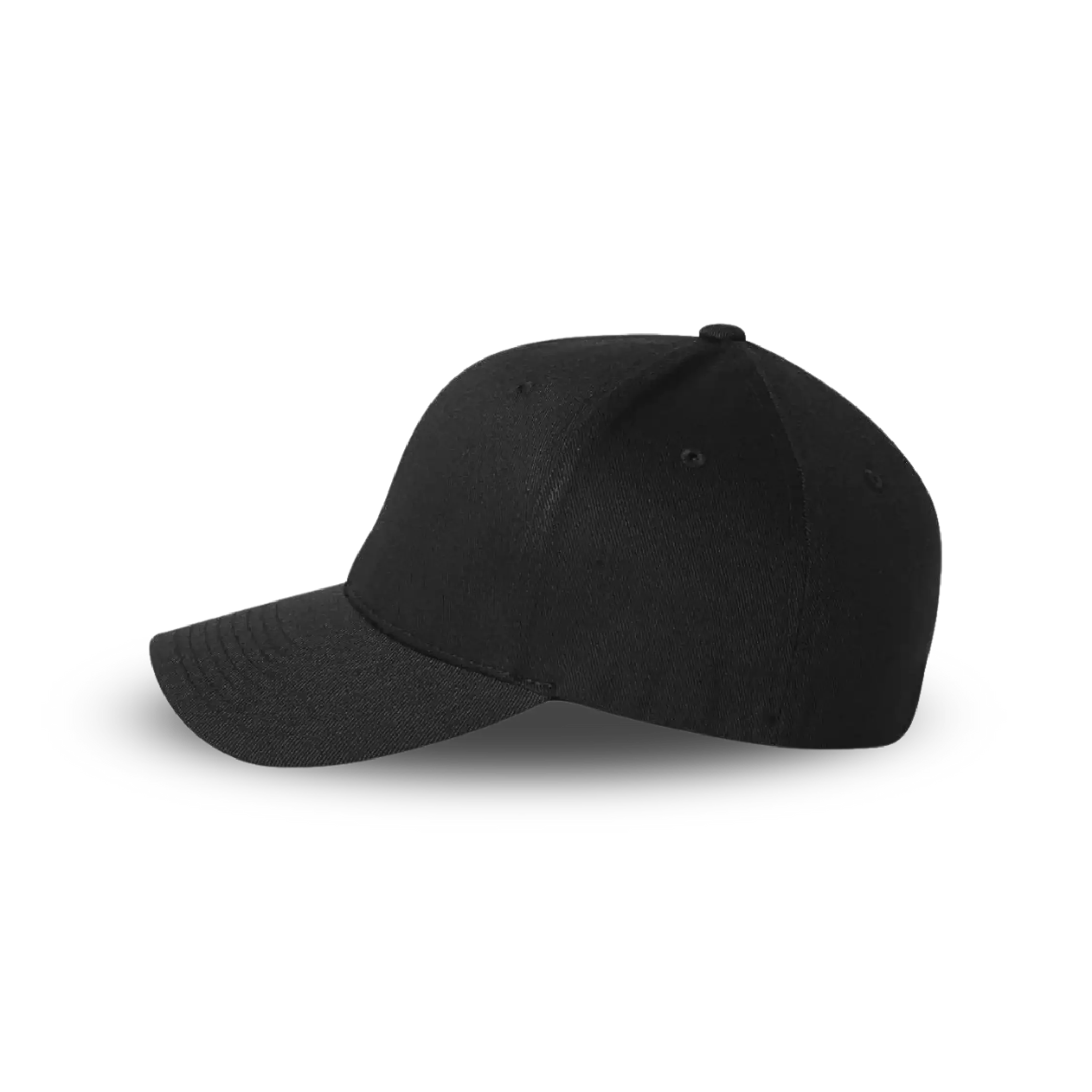
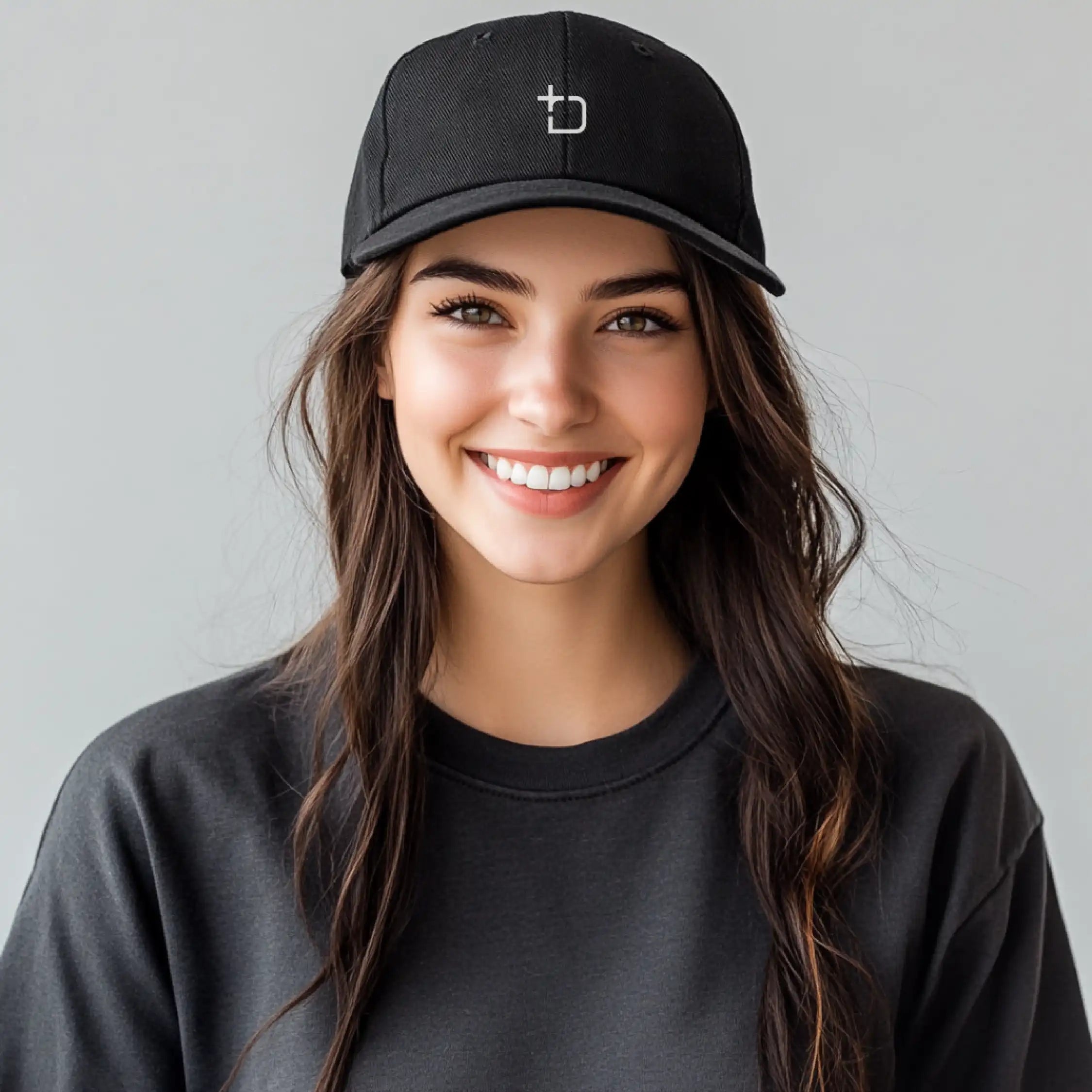
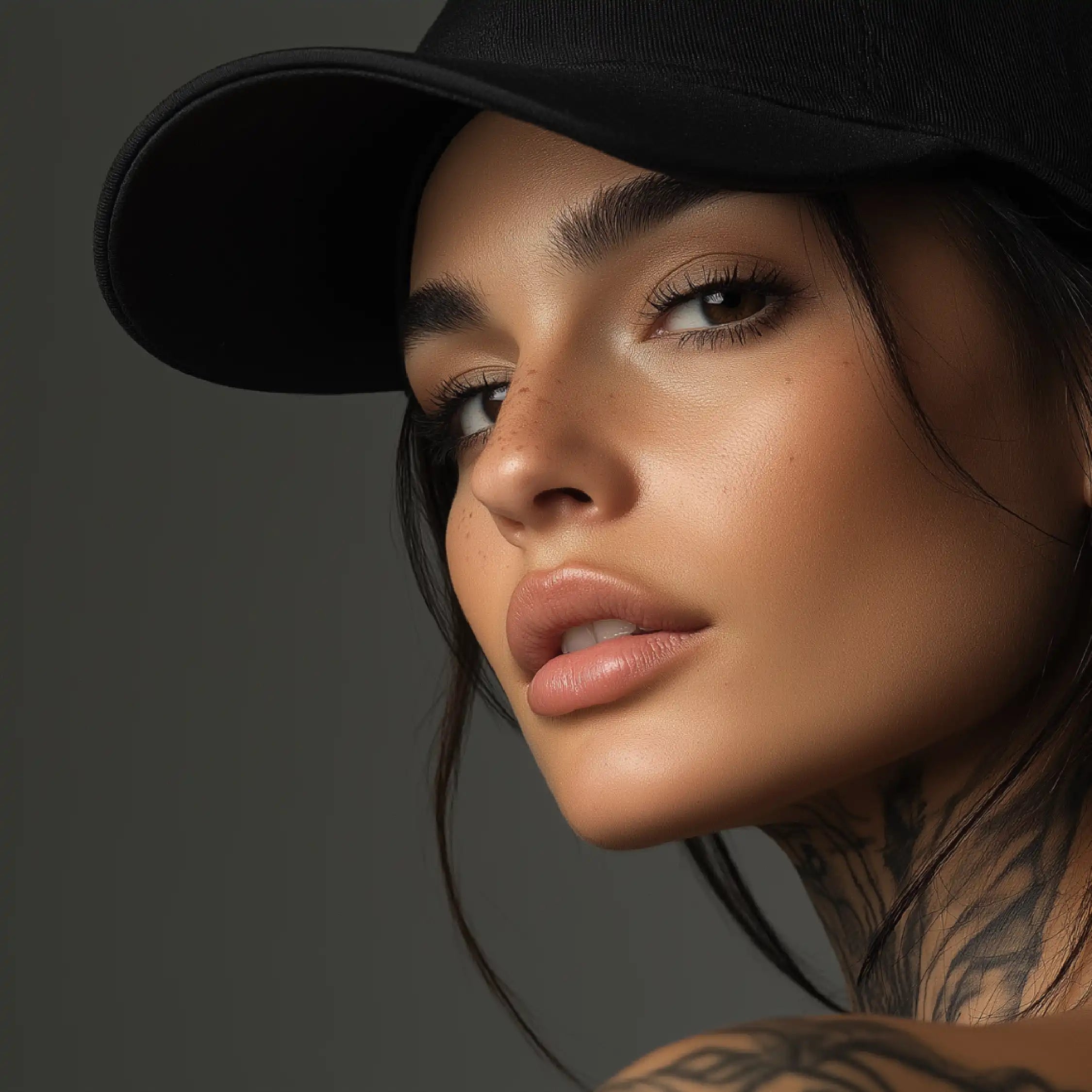
PrimeShield Fitted Cap
Built for comfort and made to last, the PrimeShield Cap combines everyday practicality with a bold, modern edge. Crafted from durable, easy-care fabric, it features a structured fit and breathable design that’s made to move with him. Whether he's out and about or taking it easy, it’s a cap that fits right into his day—effortless, reliable, and unmistakably his.
Exfoliating Foot File
Tough on dry skin, gentle on feet—built to get the job done. This durable foot file quickly buffs away rough, hardened skin, leaving feet smoother and ready to absorb the full benefits of Dermalytic. Follow with the silicone heel socks to seal in moisture and restore dry, cracked heels with minimal effort. An easy, effective routine he’ll actually use.
active ingredients in this gift pack
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, a member of the alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) family, is a well-regarded ingredient in the field of dermatology and skincare for its exfoliating and moisturizing properties. Naturally occurring in sour milk and other fermented products, lactic acid is also produced in the human body and plays a role in various metabolic processes.
In skincare, lactic acid is primarily known for its ability to exfoliate the skin gently. By breaking down the bonds that hold dead skin cells together on the skin's surface, lactic acid helps to promote the shedding of these cells, revealing fresher, brighter skin underneath. This exfoliation process improves skin texture and tone and stimulates cell renewal.
One key advantage of lactic acid over other AHAs is its moisturizing capability. Lactic acid helps increase the skin's natural moisturizing factors (NMF), essential for keeping the skin hydrated. Its unique ability to draw moisture into the skin is particularly beneficial for treating dry and dehydrated skin conditions.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: A gentle exfoliant that removes dead skin cells from the skin's surface, promoting smooth skin.
- Moisture Retention: It is a humectant that helps the skin retain moisture, improving hydration and reducing dryness.
- Collagen Stimulation: Lactic acid can stimulate collagen production in the deeper layers of the skin, aiding in skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: It helps lighten dark spots and even out skin tone, effectively treating hyperpigmentation.
- pH Balancing: Lactic acid can help balance the skin's natural pH levels, which is beneficial for maintaining a healthy skin barrier.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Lactic acid's collagen-stimulating and exfoliating properties make it effective in anti-aging treatments, reducing signs of aging like wrinkles and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: By unclogging pores and removing dead skin cells, lactic acid can help reduce acne breakouts.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Its humectant properties are beneficial in hydrating and relieving dry skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: Lactic acid treats hyperpigmentation issues, including melasma and sun damage.
- Keratosis Pilaris: It can help manage keratosis pilaris by exfoliating the excess keratin that blocks hair follicles.
References
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Stiller, M. J., et al. (1996). Topical 8% glycolic acid and 8% L-lactic acid creams for the treatment of photodamaged skin. A double-blind vehicle-controlled clinical trial. Archives of Dermatology.
- Rawlings, A. V., Davies, A., Carlomusto, M., Pillai, S., Zhang, K., Kosturko, R., ... & Watson, D. (1996). Effect of lactic acid isomers on keratinocyte ceramide synthesis, stratum corneum lipid levels and stratum corneum barrier function. Archives of Dermatological Research, 288(7), 383-390.
Urea
Urea, a naturally occurring compound in the skin, is widely recognized in dermatology and skin care for its hydrating and keratolytic properties. It is a component of the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF) and is crucial in maintaining skin hydration and barrier function.
In skin care, urea is valued for its dual action: it acts as a humectant, drawing moisture into the skin, and as a keratolytic agent, helping to break down the protein bonds between dead skin cells, leading to smoother and softer skin. This makes it particularly effective in treating dry, rough, and scaly skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and ichthyosis.
Additionally, urea has been shown to have antimicrobial properties and can aid in skin barrier repair, further underscoring its utility in treating various skin conditions.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Urea is a potent humectant, meaning it draws moisture into the skin, significantly improving hydration and maintaining skin moisture balance.
- Keratolytic Action: Urea has keratolytic properties, helping to break down the bonds between dead skin cells and aiding in the exfoliation of the skin's surface.
- Skin Barrier Function: Urea enhances the skin's barrier function, helping to prevent moisture loss and protect the skin from external irritants.
- Soothing Effect: It soothes dry, itchy, and irritated skin, providing relief from various skin conditions.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Urea is a key ingredient in many moisturizers for treating dry skin due to its excellent hydrating properties.
- Eczema and Psoriasis: It helps manage symptoms like dryness, scaling, and itching in eczema and psoriasis.
- Ichthyosis and Keratosis Pilaris: The keratolytic action of urea makes it effective in conditions characterized by excessive skin scaling, such as ichthyosis and keratosis pilaris.
- Cracked Heels and Calluses: Urea-based creams effectively soften and reduce thickened skin on heels and calluses.
- Aging Skin: It can improve skin texture and hydration in aging skin.
References
- Lodén, M. (2003). Role of topical emollients and moisturizers in the treatment of dry skin barrier disorders. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Pan, M., et al. (2013). Efficacy of topical urea in the treatment of xerosis. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Fluhr, J. W., et al. (2008). Glycerol and the skin: holistic approach to its origin and functions. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Grether-Beck, S., Felsner, I., Brenden, H., Kohne, Z., Majora, M., Marini, A., ... & Krutmann, J. (2012). Urea uptake enhances barrier function and antimicrobial defense in humans by regulating epidermal gene expression. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 132(6), 1561-1572.
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Ceramides
Ceramides, a family of lipid molecules naturally present in the skin, are integral to the structure and function of the skin barrier. They are a type of lipid that, along with cholesterol and fatty acids, forms a critical part of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin. This layer is essential for maintaining skin hydration and protecting against environmental aggressors.
Ceramides, which make up about 50% of the skin's lipid composition, play a pivotal role in maintaining the skin's barrier integrity and preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL). By doing so, they help keep the skin hydrated and supple.
The loss or reduction of ceramides in the skin barrier is associated with several dermatological conditions, including eczema and psoriasis, where the skin becomes dry, itchy, and prone to irritation and infection. Studies have shown that the application of ceramide-containing moisturizers can effectively improve skin barrier function and increase skin hydration levels.
Ceramides are particularly beneficial for aging skin, which naturally loses ceramides over time, leading to drier and more fragile skin. By replenishing the skin's ceramide content, these products can help combat the signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles.
Ceramides are integral to maintaining skin health, particularly in conditions where the skin barrier is compromised. Their role in hydrating the skin, reducing sensitivity, and improving barrier function makes them an essential component in the management of various dermatological conditions, especially eczema, psoriasis, and dry or aging skin.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function: Ceramides are critical components of the skin's lipid barrier. They help to prevent moisture loss and protect against environmental aggressors like pollutants and irritants.
- Hydration: By maintaining the barrier integrity, ceramides keep the skin hydrated, preventing dryness and keeping the skin supple.
- Reducing Skin Sensitivity: They play a role in reducing skin sensitivity and irritation, helping to calm inflamed and reactive skin.
- Anti-aging Properties: Ceramides can improve skin elasticity and firmness, helping to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Wound Healing: There is evidence to suggest that ceramides can aid in the skin's natural wound healing process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis: Ceramides are often used in the treatment of eczema and atopic dermatitis, where the skin barrier is compromised, leading to dryness, itching, and inflammation.
- Psoriasis: They can help in managing psoriasis by maintaining skin hydration and barrier function, reducing scaling and dryness.
- Aging Skin: Ceramide-containing products are beneficial in anti-aging regimens due to their ability to improve skin barrier function and elasticity.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): In the treatment of dry skin, ceramides help in restoring skin hydration and barrier function.
- Sensitive Skin: Products containing ceramides are suitable for sensitive skin as they help to restore the skin's natural barrier and reduce irritation.
References
- Del Rosso, J. Q., & Levin, J. (2011). The clinical relevance of maintaining the functional integrity of the stratum corneum in both healthy and disease-affected skin. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Farwanah, H., Wohlrab, J., Neubert, R. H. H., & Raith, K. (2005). Ceramides and skin function. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Di Nardo, A., Wertz, P., Giannetti, A., & Seidenari, S. (1998). Ceramide and cholesterol composition of the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica.
d-Panthenol
d-Panthenol's multifaceted effects on skin hydration, barrier strengthening, and wound healing make it a valuable component in the management of various dermatological conditions, from dry skin to post-procedure care.
d-Panthenol, also known as pro-vitamin B5, is a popular dermatological ingredient due to its beneficial effects on the skin. Here's a brief overview of its physiological effects and roles in managing various skin conditions:
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: d-Panthenol is a humectant, meaning it helps to attract and retain moisture in the skin. This leads to increased skin hydration, which can improve skin softness and elasticity.
- Wound Healing and Repair: It plays a role in the synthesis of lipids and proteins, essential for skin repair. d-Panthenol has been shown to accelerate re-epithelialization in wound healing.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effect: d-Panthenol can reduce inflammation, making it beneficial in treating skin irritations and erythema.
- Skin Barrier Strengthening: By enhancing the synthesis of lipids and proteins, d-Panthenol contributes to the strengthening of the skin's barrier function, protecting against irritants and environmental damage.
- Soothing and Softening: It soothes the skin and makes it feel softer and smoother, which can be particularly beneficial for dry or rough skin textures.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Minor Wounds and Skin Irritations: Due to its role in skin repair and anti-inflammatory properties, d-Panthenol is used in the treatment of minor wounds, cuts, and skin irritations.
- Dermatitis and Eczema: It helps in managing conditions like dermatitis and eczema by reducing inflammation and enhancing skin barrier function.
- Dry Skin Conditions (Xerosis): Its moisturizing properties make it effective in treating dry skin, providing relief from itching and scaling.
- Post-procedure Care: d-Panthenol is often used in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments or chemical peels, to aid in skin recovery and reduce inflammation.
References
- Proksch, E., & Nissen, H. P. (2002). Dexpanthenol enhances skin barrier repair and reduces inflammation after sodium lauryl sulphate-induced irritation. Journal of Dermatological Treatment.
- Ebner, F., Heller, A., Rippke, F., & Tausch, I. (2002). Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Camargo, F. B. Jr, Gaspar, L. R., & Maia Campos, P. M. B. G. (2011). Skin moisturizing effects of panthenol-based formulations. Journal of Cosmetic Science.
Lipid Bilayer Technology
Lipid bilayer technology in dermatology focuses on mimicking and reinforcing the skin's natural lipid barrier, which is vital for maintaining skin health and integrity.
Physiological Effects
- Reinforcement of Skin Barrier: Lipid bilayer technology aims to replicate the skin's natural barrier, particularly beneficial for damaged or compromised skin. This reinforcement helps in reducing transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and enhancing skin hydration.
- Restoration of Lipid Composition: It helps in replenishing the essential lipids that are often deficient in certain skin conditions, thereby restoring the skin's natural protective barrier.
- Improvement in Skin Texture and Hydration: By restoring the lipid bilayer, this technology improves skin texture and overall hydration, leading to healthier, more resilient skin.
- Reduction of Inflammation and Irritation: It can help in reducing inflammation and irritation, particularly in conditions where the skin barrier is compromised.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Lipid bilayer technology is particularly beneficial in managing eczema, as it helps in restoring the deficient skin barrier function, reducing dryness, and controlling flare-ups.
- Psoriasis: In psoriasis, where the skin barrier is also disrupted, this technology aids in hydrating the skin and reducing scaling.
- Aging Skin: The aging skin, which naturally loses lipids over time, benefits from lipid bilayer technology as it helps in maintaining skin hydration and elasticity.
- Dry Skin Conditions (Xerosis, Ichthyosis): Enhancing the skin’s lipid content can significantly improve symptoms of dryness and scaling in these conditions.
- Sensitive Skin: For sensitive skin types, lipid bilayer technology can provide a gentle and effective way to strengthen the skin barrier without causing irritation.
References
- Del Rosso, J. Q., & Levin, J. (2011). The Clinical Relevance of Maintaining the Functional Integrity of the Stratum Corneum in both Healthy and Disease-affected Skin. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Rawlings, A. V., & Harding, C. R. (2004). Moisturization and Skin Barrier Function. Dermatologic Therapy.
- Man, M. Q., Xin, S. J., Song, S. P., Cho, S. Y., Zhang, X. J., Tu, C. X., ... & Elias, P. M. (2009). Variation of Skin Surface pH, Sebum Content and Stratum Corneum Hydration with Age and Gender in a Large Chinese Population. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
Medilan™'s unique formulation and hypoallergenic properties make it a valuable component in the management of various dermatological conditions, particularly for hydrating and soothing sensitive and dry skin.
Medilan™, a ultra-refined, hypoallergenic medical grade lanolin, has proven to be very beneficial for managing dermatological conditions. Below is a brief overview of its physiological effects and roles in managing various skin conditions:
Physiological Effects of Medilan™
- Emollient: Medilan™ is an excellent emollient, helping to soften and smooth the skin by retaining moisture. It creates an occlusive barrier, which reduces transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
- Moisturizing: It is highly effective in moisturizing dry and rough skin, enhancing skin hydration by trapping and sealing in moisture.
- Hypoallergenic: Medilan™ is ultra-purified to minimize the risk of allergic reactions, making it suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Wound Healing: Medilan™ aids in the healing process of minor cuts, abrasions, and burns by maintaining a moist wound environment.
- Skin Barrier Function: It enhances the skin's barrier function, protecting against environmental irritants and reducing the risk of skin infections.
- Lipid Replenishment: Medilan™ mimics the lipids found in human skin, helping to restore the lipid barrier of the skin, especially beneficial in dry and chapped skin conditions.
- Skin Penetration and Hydration: It has the ability to penetrate the skin and aid in water retention in the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin, thus enhancing hydration.
- Occlusive Properties: Medilan™ helps in reducing transepidermal water loss by forming a barrier on the skin surface, thereby retaining moisture and improving skin barrier function.
Role in Managing Dermatological Conditions:
- Eczema and Dry Skin Conditions: Due to its soothing, hydrating, and occlusive properties, Medilan™ is a valuable ingredient in treating eczema and other dry skin conditions.
- Wound Healing: While primarily used for its emollient effects, the properties of Medilan™ also aid in the healing of minor wounds and skin irritations.
- Sensitive Skin Care: Its hypoallergenic nature makes it suitable for use in individuals with sensitive skin, reducing the risk of irritation or allergic reactions.
- Nipple Care in Breastfeeding: Soothes and heals cracked and sore nipples in breastfeeding mothers.
- Chapped Lips and Skin: It is effective in treating chapped lips and skin, providing a barrier that seals in moisture and protects from harsh weather conditions.
References
- Lodén, M., & Maibach, H. I. (2000). Dry skin and moisturizers: chemistry and function. CRC Press.
- Suleman, H., et al. (2000). Role of lanolin in managing eczema and dry skin conditions. Community Nurse.
- DiNardo, J. C. (2000). Is lanolin allergy a myth? Dermatitis.
- Stone, L. (2000). Medilan: a hypoallergenic lanolin for emollient therapy. British Journal of Nursing.
- ResearchGate Article on Medilan™ highlighting its role in skin care and emollient therapy.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide offers several benefits for the skin, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It reduces the redness and inflammation associated with acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Additionally, niacinamide's ability to improve the skin's barrier function benefits all skin types, particularly those with eczema or mature skin.
Another significant benefit of niacinamide is its role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Studies have shown that it can decrease the transfer of melanin to the epidermis, helping to fade dark spots and even out skin tone.
Niacinamide also plays a role in reducing the visible signs of aging. It has been found to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity, reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Its antioxidant properties further protect the skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV radiation, which contribute to premature aging.
The efficacy of niacinamide and its ability to address multiple skin concerns simultaneously has led to its growing popularity in both over-the-counter and prescription skincare formulations.
Physiological Effects
- Barrier Function Enhancement: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s barrier function by increasing the production of ceramides, lipids that keep the skin hydrated and protect against environmental damage.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It has notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in reducing redness and inflammation associated with acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: Niacinamide helps regulate sebum production, which controls excess oiliness and can benefit acne-prone skin.
- Hyperpigmentation Reduction: It reduces hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, leading to an even skin tone.
- Anti-aging Effects: Niacinamide helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen production and improving skin elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: It has antioxidant properties, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental aggressors like UV radiation and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne and Oily Skin: Niacinamide effectively manages acne and oily skin by regulating sebum and reducing inflammation.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: Its ability to reduce melanin transfer benefits it in treating hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Aging Skin: Niacinamide targets wrinkles and loss of firmness.
- Skin Barrier Disorders: Niacinamide is beneficial in treating skin barrier disorders like atopic dermatitis and eczema by enhancing barrier function and hydration.
- Photodamage and Skin Protection: It helps mitigate the effects of photodamage and provides some degree of protection against environmental damage.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Snaidr, V. A., Damian, D. L., & Halliday, G. M. (2019). Nicotinamide for photoprotection and skin cancer chemoprevention: A review of efficacy and safety. Experimental Dermatology.
- Navarrete-Solís, J. et al. (2011). A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found throughout the body's connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. Most abundantly present in the skin, eyes, and synovial fluid, HA is renowned for its exceptional capacity to retain moisture — a single gram can hold up to six liters of water.
In skincare, the primary appeal of hyaluronic acid lies in its unparalleled hydrating abilities. As a humectant, HA attracts and retains moisture from the environment, providing intense hydration to the skin. This hydrating property contributes significantly to maintaining skin plumpness, suppleness, and elasticity.
Beyond hydration, hyaluronic acid also plays a vital role in skin repair and regeneration. It supports the skin's healing and repair processes, and its anti-inflammatory properties help calm irritated skin. Moreover, HA's ability to promote collagen production, a crucial protein for skin elasticity, further underscores its anti-aging benefits.
The molecular size of hyaluronic acid influences its skin penetration and efficacy. High-molecular-weight HA remains on the skin's surface, providing hydration and forming a barrier against moisture loss. In contrast, low-molecular-weight HA penetrates deeper into the skin's layers, offering more profound hydrating and rejuvenating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's remarkable ability to hydrate, improve skin elasticity, aid in wound healing, and provide antioxidant protection makes it valuable in managing various dermatological conditions, particularly aging, dryness, and sensitive skin.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water, significantly enhancing skin hydration and leading to plumper, more hydrated skin.
- Skin Elasticity and Wrinkle Reduction: By increasing skin moisture, it improves skin elasticity, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and gives the skin a more youthful appearance.
- Wound Healing: It plays a role in wound healing due to its ability to regulate inflammation levels and signal the body to build more blood vessels in the damaged area.
- Barrier Enhancement: Hyaluronic acid helps reinforce the skin's natural barriers, protecting against environmental factors and retaining moisture.
- Antioxidant Properties: It provides antioxidant defense against free-radical damage from the sun and pollution.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Its ability to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity makes it popular in anti-aging skincare products.
- Dry Skin: Hyaluronic acid is beneficial in treating dry skin conditions by providing intense hydration.
- Wound Care: Its role in wound healing is leveraged in post-procedure care, such as after laser treatments, and in healing minor cuts and abrasions.
- Acne Scars: It can help treat acne scars by promoting skin regeneration and reducing inflammation.
- Sensitive Skin: Hyaluronic acid is suitable for sensitive skin due to its gentle nature. It provides hydration without irritating.
References
- Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2012). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-endocrinology.
- Jegasothy, S. M., Zabolotniaia, V., & Bielfeldt, S. (2014). Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology.
- Wollina, U., & Abdel-Naser, M. B. (2019). Hyaluronic acid in the treatment and prevention of skin diseases: Molecular biological, pharmaceutical and clinical aspects. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology.
Infraguard™
Infraguard™ is a novel and powerful antioxidant powerhouse designed to protect the skin from the potentially harmful effects of electromagnetic radiation, specifically from 5G networks, blue light, and other environmental stressors. It shields the skin against oxidative stress and inflammation, prevents premature aging, and maintains overall health.
Infraguard® is a multifunctional ingredient that extends beyond traditional sun protection. It addresses the broader spectrum of light-induced skin damage and oxidative stress, provides DNA protection, and offers anti-aging benefits. Its inclusion in the DermExcel sunscreens represents an advanced step in comprehensive skin care, targeting UV rays and the often-overlooked infrared and blue light, ensuring a more holistic approach to maintaining skin health and appearance.
Physiological Effects
- Protection Against Blue Light and Infrared (IR) Radiation: Infraguard is formulated to shield the skin from the harmful effects of blue light and IR radiation, which can lead to premature skin aging and damage.
- Antioxidant Properties: It has strong antioxidant capabilities, helping to neutralize free radicals induced by environmental stressors such as pollution, IR, and blue light.
- Anti-Aging Benefits: By protecting against IR radiation and mitigating oxidative stress, Infraguard helps to prevent signs of aging like wrinkles and loss of skin elasticity.
- Skin Barrier Protection: Infraguard strengthens the skin's natural barrier, enhancing its resilience against environmental factors.
- DNA Protection: Infraguard™ aids in shielding the DNA in skin cells from damage caused by environmental aggressors. This is crucial in maintaining the integrity of skin cells and preventing mutations that can lead to skin aging and other skin-related issues.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Preventing Photoaging: Infraguard's ability to protect against IR and blue light makes it beneficial in preventing photoaging, a key concern in modern dermatology. Infrared light can penetrate deeper into the skin than UV rays, potentially leading to increased collagen degradation and skin laxity. Infraguard® helps mitigate these effects.
- Combatting Environmental Stressors: Its antioxidant properties protect the skin from various environmental pollutants and stressors.
- Supporting Skin Health: Infraguard contributes to overall skin health by improving the skin's barrier function and providing antioxidant support.
- Suitability for Diverse Skin Conditions: Given its protective and anti-aging properties, Infraguard is suitable for use in various dermatological conditions, especially environmental damage and aging.
References
- Kappler, Katharina et al. "Development of an in Vitro Assay to Evaluate the Biological Impact of 5G Technology on Human Skin. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 2022, vol. 12, pp. 100-108. DOI: 10.4236/jcdsa.2022.122009.
- Extensive references cited within the research article including studies on 5G technology, health effects, and skin biology.
products in your gift pack







Please login to view the price
login
Ingrown hair

Body Acne

Keratosis Pilaris

Rough Skin

cracked heels
A potent and clinically formulated ointment that effectively treats calloused, rough, and dry skin. It's more than a standard moisturizer; it exfoliates dead skin cells and replenishes moisture. The product creates an optimal environment for skin health, leading to a smoother complexion.
Key ingredients include 10% Glycolic acid for exfoliation, 10% Lactic acid for removing dead cells, and 20% Urea for lasting hydration. Its "cream-ointment" base balances efficacy and application comfort. Dermalytic's medical-grade formula and scientific skincare approach visibly improve skin texture, giving users a renewed sense of confidence and comfort.
Note: Dermalytic is too potent for facial use.
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is highly acclaimed for its remarkable exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. Its small molecular size enables deep skin penetration, fostering efficient exfoliation at the cellular level.
Glycolic acid’s water solubility allows it to penetrate the upper layers of the skin easily. Its primary mechanism of action involves weakening the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding, and revealing the newer, healthier skin beneath. This process of accelerated cell turnover is instrumental in addressing a range of skin concerns, from aging signs like fine lines and wrinkles to texture irregularities and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic acid's efficacy extends beyond mere exfoliation. It's also recognized for stimulating collagen production, a crucial protein in maintaining skin's elasticity and firmness. This aspect contributes to its anti-aging benefits. Furthermore, its hydrating properties add to its appeal, as they help increase the skin's capacity to retain moisture, leading to a more supple and vibrant complexion.
Clinical studies have consistently supported glycolic acid's role in improving skin appearance. Research indicates significant improvements in skin texture and pigmentation and the visible reduction of wrinkles and fine lines with glycolic acid.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is a powerful exfoliant. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells on the skin’s surface, facilitating their removal and revealing newer, healthier skin underneath.
- Increased Collagen Production: It stimulates collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and firmness. This action helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhanced Skin Hydration: Glycolic acid improves the skin's ability to retain moisture, enhancing hydration and a more plump, vibrant skin appearance.
- Skin Brightening: Removing dead skin cells can brighten the complexion and reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
- Improved Skin Texture: Regular use of glycolic acid can lead to smoother, more even textured skin, making it beneficial for conditions like keratosis pilaris.
- Acne Treatment: Its exfoliating properties help in unclogging pores, thereby reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Glycolic acid is widely used in anti-aging products to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: It helps manage acne by exfoliating the skin and removing blockage from pores.
- Hyperpigmentation: It effectively treats hyperpigmentation by accelerating the removal of hyperpigmented skin cells.
- Textural Irregularities: Glycolic acid can improve skin texture and is beneficial for treating keratosis pilaris and other conditions of rough skin.
- Sun-Damaged Skin: It helps rejuvenate sun-damaged skin by accelerating cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
References
- Bernstein, E. F. (2001). Glycolic acid treatment increases type I collagen mRNA and hyaluronic acid content of human skin. Dermatologic Surgery.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Sharad, J. (2013). Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 35(3), 388-391.
Urea
Urea, a naturally occurring compound in the skin, is widely recognized in dermatology and skin care for its hydrating and keratolytic properties. It is a component of the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF) and is crucial in maintaining skin hydration and barrier function.
In skin care, urea is valued for its dual action: it acts as a humectant, drawing moisture into the skin, and as a keratolytic agent, helping to break down the protein bonds between dead skin cells, leading to smoother and softer skin. This makes it particularly effective in treating dry, rough, and scaly skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and ichthyosis.
Additionally, urea has been shown to have antimicrobial properties and can aid in skin barrier repair, further underscoring its utility in treating various skin conditions.
Physiological Effects
- Hydration: Urea is a potent humectant, meaning it draws moisture into the skin, significantly improving hydration and maintaining skin moisture balance.
- Keratolytic Action: Urea has keratolytic properties, helping to break down the bonds between dead skin cells and aiding in the exfoliation of the skin's surface.
- Skin Barrier Function: Urea enhances the skin's barrier function, helping to prevent moisture loss and protect the skin from external irritants.
- Soothing Effect: It soothes dry, itchy, and irritated skin, providing relief from various skin conditions.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Urea is a key ingredient in many moisturizers for treating dry skin due to its excellent hydrating properties.
- Eczema and Psoriasis: It helps manage symptoms like dryness, scaling, and itching in eczema and psoriasis.
- Ichthyosis and Keratosis Pilaris: The keratolytic action of urea makes it effective in conditions characterized by excessive skin scaling, such as ichthyosis and keratosis pilaris.
- Cracked Heels and Calluses: Urea-based creams effectively soften and reduce thickened skin on heels and calluses.
- Aging Skin: It can improve skin texture and hydration in aging skin.
References
- Lodén, M. (2003). Role of topical emollients and moisturizers in the treatment of dry skin barrier disorders. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Pan, M., et al. (2013). Efficacy of topical urea in the treatment of xerosis. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.
- Fluhr, J. W., et al. (2008). Glycerol and the skin: holistic approach to its origin and functions. British Journal of Dermatology.
- Grether-Beck, S., Felsner, I., Brenden, H., Kohne, Z., Majora, M., Marini, A., ... & Krutmann, J. (2012). Urea uptake enhances barrier function and antimicrobial defense in humans by regulating epidermal gene expression. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 132(6), 1561-1572.
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, a member of the alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) family, is a well-regarded ingredient in the field of dermatology and skincare for its exfoliating and moisturizing properties. Naturally occurring in sour milk and other fermented products, lactic acid is also produced in the human body and plays a role in various metabolic processes.
In skincare, lactic acid is primarily known for its ability to exfoliate the skin gently. By breaking down the bonds that hold dead skin cells together on the skin's surface, lactic acid helps to promote the shedding of these cells, revealing fresher, brighter skin underneath. This exfoliation process improves skin texture and tone and stimulates cell renewal.
One key advantage of lactic acid over other AHAs is its moisturizing capability. Lactic acid helps increase the skin's natural moisturizing factors (NMF), essential for keeping the skin hydrated. Its unique ability to draw moisture into the skin is particularly beneficial for treating dry and dehydrated skin conditions.
Physiological Effects
- Exfoliation: A gentle exfoliant that removes dead skin cells from the skin's surface, promoting smooth skin.
- Moisture Retention: It is a humectant that helps the skin retain moisture, improving hydration and reducing dryness.
- Collagen Stimulation: Lactic acid can stimulate collagen production in the deeper layers of the skin, aiding in skin firmness and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Skin Brightening: It helps lighten dark spots and even out skin tone, effectively treating hyperpigmentation.
- pH Balancing: Lactic acid can help balance the skin's natural pH levels, which is beneficial for maintaining a healthy skin barrier.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Aging Skin: Lactic acid's collagen-stimulating and exfoliating properties make it effective in anti-aging treatments, reducing signs of aging like wrinkles and age spots.
- Acne-Prone Skin: By unclogging pores and removing dead skin cells, lactic acid can help reduce acne breakouts.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Its humectant properties are beneficial in hydrating and relieving dry skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: Lactic acid treats hyperpigmentation issues, including melasma and sun damage.
- Keratosis Pilaris: It can help manage keratosis pilaris by exfoliating the excess keratin that blocks hair follicles.
References
- Smith, W. P. (1996). Epidermal and dermal effects of topical lactic acid. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.
- Stiller, M. J., et al. (1996). Topical 8% glycolic acid and 8% L-lactic acid creams for the treatment of photodamaged skin. A double-blind vehicle-controlled clinical trial. Archives of Dermatology.
- Rawlings, A. V., Davies, A., Carlomusto, M., Pillai, S., Zhang, K., Kosturko, R., ... & Watson, D. (1996). Effect of lactic acid isomers on keratinocyte ceramide synthesis, stratum corneum lipid levels and stratum corneum barrier function. Archives of Dermatological Research, 288(7), 383-390.






Please login to view the price
loginReveal softer, healthier-looking feet with this high-performance Exfoliating Foot File. Effectively smooths and refines rough, dry areas to restore skin's natural softness.
The coarse grinding surface efficiently removes calluses, dead skin, and corns, while precision holes help minimize friction and allow for cleaner, more effective exfoliation.
Features:
- Dual-action stainless steel surface for long-lasting durability
- Coarse grit ideal for thick, hardened skin
- Ergonomic, non-slip handle for comfortable, controlled use
- Easy to clean and reusable
For best results, pair with Dermalytic and Silicone Heel Guards to achieve professional-grade care at home.






Please login to view the price
loginSIZE: 50 mL

Antioxidant

anti-aging

DNA repair

sun protection

Moisturizing
A pioneering sunscreen offering superior protection against the sun while preserving your skin's cellular and DNA health. The innovative formula exceeds standard UV protection, guarding against UVA, UVB, damaging infrared rays, and blue light. Offering wide-ranging protection bolsters your skin's restorative abilities, promoting a healthier and more resilient complexion.
Designed to be fragrance-free and anti-comedogenic, Dermdefence SPF 50 ensures no skin irritation or pore clogging, making it an excellent choice for those with skin conditions like Acne, Rosacea, or Eczema. Its lightweight, non-greasy texture provides easy application and rapid absorption, without leaving a white cast.
Dermdefence SPF 50 also serves as a primer, providing a smooth finish for easy makeup application and ensuring a flawless look all day. Dermdefence SPF 50 provides unparalleled sun protection that will shield your skin and nurture its unique needs, maintaining its health and radiance.
Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 is a potent ingredient that offers comprehensive skin health and appearance benefits. Its role in energy production and its antioxidant and anti-aging properties make it invaluable for photoprotection, anti-aging, and overall skin vitality. Its incorporation into DermExcel sunscreen represents a holistic approach to skin health, addressing protective and restorative needs.
Physiological Impact
- Skin Barrier Enhancement: CoQ10 contributes to the strength and health of the skin barrier, improving its ability to retain moisture and protect against external irritants and pollutants.
- Skin Repair and Regeneration: It supports the skin's natural ability to repair itself and regenerate, maintaining a healthy, youthful appearance. This is particularly beneficial in mature skin, where natural levels of CoQ10 may be depleted.
Pharmacological Advantages
- Anti-Aging Effects: CoQ10's antioxidant properties contribute to its anti-aging effects. By reducing oxidative stress, it helps to minimize the visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines.
- Photoprotection: It enhances the skin's defense against photoaging caused by exposure to UV rays. CoQ10 helps to mitigate the degradation of collagen and elastin, proteins essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
Biochemical Benefits
- Cellular Energy Production: CoQ10 plays a crucial role in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is essential for the production of ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell. This function is vital for maintaining the health and vitality of skin cells.
- Antioxidant Properties: It acts as a lipophilic antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. This is particularly important in the skin, which is frequently exposed to oxidative stress from environmental factors like UV radiation.
Vitamin E
The fat-soluble Vitamin E's benefits in maintaining skin health and appearance are well-acknowledged in both cosmetic and clinical dermatology. Comprising a group of eight compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, Vitamin E is known for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage.
Vitamin E is celebrated in skincare for its ability to neutralize free radicals caused by environmental stressors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals can lead to premature skin aging, making Vitamin E a valuable ingredient in anti-aging skincare products. Its antioxidant action helps to protect the skin from damage, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and improve skin texture and tone.
Additionally, Vitamin E is known for its moisturizing benefits. It helps to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce moisture loss, and keep the skin hydrated and supple. This makes it especially beneficial for dry and damaged skin.
Vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial in soothing and calming irritated skin. This has implications for conditions such as dermatitis and acne, where inflammation plays a key role.
Physiological Effects
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes harmful free radicals in the skin, preventing oxidative stress and damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Moisturization: It has moisturizing properties, helping to improve skin hydration and alleviate dryness.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin E may assist in the skin's healing process, although its efficacy in wound healing is still a subject of research.
- Photoprotection: While not a sunscreen, it can provide some degree of photoprotection by strengthening the skin's defense against UV-induced damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce skin inflammation and is beneficial in managing conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Skin Aging: Its antioxidant properties make it useful in anti-aging skincare products to protect against free radical damage and improve skin appearance.
- Dry Skin Conditions: Vitamin E's moisturizing effects are beneficial in treating dry skin and improving overall skin texture.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: It can be helpful in soothing inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
- Sun Protection and Repair: Vitamin E is included in sunscreens and after-sun products for its ability to mitigate sun damage.
- Scar Treatment: Some studies suggest Vitamin E may help reduce the appearance of scars, although evidence is mixed.
References
- Thiele, J. J., Hsieh, S. N., & Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. (1998). Vitamin E: Critical Review of Its Current Use in Cosmetic and Clinical Dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery, 24(7), 805–813.
- Ratz-Łyko, A., & Arct, J. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties of active skin care ingredients. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 9(9), 36–40.
- Keen, M. A., & Hassan, I. (2016). Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
- Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S., & Thiele, J. (2007). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- Nachbar, F., & Korting, H. C. (1995). The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. Journal of Molecular Medicine.
Broad Spectrum Filters
Tinosorb® M and Tinosorb® S represent sophisticated advancements in sun protection technology.
Tinosorb® M
- Biochemical Action: A unique UV filter due to its ability to function through absorption, reflection, and scattering of UV rays.
- Physiological Impact: The triple-action mechanism of Tinosorb® M offers comprehensive sun protection. By mitigating the penetration of both UVA and UVB rays, it significantly reduces the risk of DNA damage, photoaging, and carcinogenesis. Its ability to remain on the skin's surface reduces systemic exposure, making it a safer option with minimal potential for irritation or allergic reactions.
Tinosorb® S
- Biochemical Action: A broad-spectrum UV filter with a molecular structure that effectively absorbs both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, it enhances the photostability of other UV filters, making the sunscreen formulation more effective over time.
- Physiological Impact: By providing extensive UVA and UVB protection, Tinosorb® S plays a crucial role in preventing short-term sun damage like sunburn and long-term risks such as skin aging and skin cancer. Its photostability ensures sustained protection during sun exposure, and its compatibility with other UV filters means it can be used to formulate sunscreens that are both effective and suitable for sensitive skin.
Sunscreen
Using sunscreen is a fundamental aspect of skin care and preventive dermatology. It's essential for reducing the risk of skin cancers and photoaging and maintaining overall skin health in the face of constant exposure to UV radiation.
Sunscreen is a vital skincare product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Two primary types of UV radiation affect the skin: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging and long-term skin damage, whereas UVB rays cause sunburn and play a key role in developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen products work by either absorbing, reflecting, or scattering sunlight. They contain chemical compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into a small amount of heat or physical compounds (like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) that act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV light away from the skin.
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF). SPF indicates how well the sunscreen protects against UVB rays. For example, an SPF of 30 means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn than without sunscreen. However, it's important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% UV rays.
Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can reduce the risk of skin cancer, prevent sunburn, and slow down the skin's aging process.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Prevention of Sunburn: Sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. This reduces the immediate risk of skin damage and discomfort.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Regular use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, especially melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.
- Prevention of Photoaging: Sunscreen also shields the skin from UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for photoaging, including wrinkles, leathery skin, and sunspots.
- Protection Against Photosensitivity: Sunscreen helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure for individuals with photosensitive skin conditions like lupus or rosacea.
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: It aids in preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma, conditions exacerbated by sun exposure.
- General Skin Health: Sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health and integrity by protecting the skin from UV damage.
References
- Burnett, M. E., & Wang, S. Q. (2011). Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.
- Green, A. C., et al. (2011). Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: randomized trial follow-up. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine.













Please login to view the price
login
fitted

crease-resistant

colour-fast

stain-resistant
Elevate your headwear game with the bold style and high-performance functionality of the PrimeShield Cap. Crafted from durable 100% polyester honeycomb fabric, this fitted cap is designed for long-lasting wear and effortless care. Its crease-resistant, colorfast, and stain-resistant properties make it ideal for everyday use while retaining its sleek and polished look.
Engineered for ultimate comfort, the PrimeShield Cap features an elasticated sweatband for a secure, tailored fit and a lightweight construction that ensures breathability throughout the day. The 6-panel structured peak provides a sharp, refined shape, complemented by meticulous detailing such as six rows of stitching and four embroidered eyelets for added ventilation.
Combining practicality with bold, modern design, the PrimeShield Cap is the perfect choice for those who seek a balance of style, comfort, and performance in their headwear.






Please login to view the price
loginKeep your keys secure and effortlessly stylish with the Genuine Leather DermExcel Key Ring. It is a timeless accessory crafted for everyday refinement. Made from premium genuine leather, it combines durability with a soft, luxurious feel.
The minimalistic design is elevated by subtle branding, making it a versatile piece that complements both casual and professional settings. Whether clipped to your keys or tucked into your bag, this key ring is a quiet statement of confidence.
Size: L13.5cm x W3.5cm
Testimonials
This hand treatment is the best for dry hands work perfectly for your hands. Best product for your hands.
This was an excellent gift and I needed all the products put together in the gift.
I absolutely love these products, I’ve been using the range for 3 years now and will it change!!
Love it!