Scalp Treatment
Please login to view the price
loginSIZE: 120 mL

healthy scalp

anti-dundruff

↓ inflammation

oil control

Itch Relief
A maximum-strength medicated scalp treatment relieves the itching, irritation, redness, flaking, and scaling associated with dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis.
A powerful formula that combines 2% Salicylic acid and 2% Zinc Pyrithione for maximum effectiveness and life-changing results.
Zinc Pyrithione, an antifungal, antimicrobial, and antibacterial agent, works by reducing the amount of fungus that triggers inflammation and scaling. Zinc Pyrithione also treats pityrosporum folliculitis (fungal acne) on the face and other body parts.
Salicylic acid gently exfoliates the scalp, removing dead skin cells and excess oil, contributing to dandruff and itchiness. As a result, it unclogs hair follicles, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione, a compound with potent antifungal and antibacterial properties, has established itself as a cornerstone in the treatment of various skin conditions, particularly those involving Malassezia yeast. Its effectiveness against seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, which are often associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia species, makes it a key ingredient for many dermatological conditions.
Zinc pyrithione’s mode of action is multifaceted, primarily targeting the membrane of fungi and bacteria, thereby disrupting their growth and replication. One of its significant mechanisms involves inhibiting fungal cell membrane transport by blocking the energy production pathway, which is crucial for cell survival.
In Malassezia, yeast, a natural inhabitant of the skin flora, can overgrow and cause conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff; zinc pyrithione's antifungal action is particularly beneficial. It reduces the yeast population on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with its overgrowth, such as flaking, irritation, and redness.
Its efficacy in treating seborrheic dermatitis is attributed to its ability to reduce the Malassezia count, diminish inflammatory responses, and soothe the skin. Similarly, in dandruff, which is often linked to an excess of Malassezia, zinc pyrithione effectively reduces flaking and itchiness, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
The efficacy of zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is well-documented. Its safety profile and efficacy have been confirmed by numerous studies, with significant improvements observed in both scalp and skin conditions following regular use.
Physiological Effects
- Antifungal Activity: It is effective against a range of fungi, including those that cause dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Zinc Pyrithione inhibits the division of fungal cells, reducing their proliferation.
- Antibacterial Properties: This compound also exhibits antibacterial activity, making it useful in treating and preventing bacterial skin infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc Pyrithione can reduce inflammation, which is beneficial in alleviating symptoms of various inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps in regulating sebum production, which can be beneficial for oily skin and conditions like acne.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione is a common ingredient in anti-dandruff shampoos and is effective in controlling the flaking and itching associated with these conditions.
- Psoriasis: It can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis, particularly in reducing scaling and redness.
- Acne: Due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc Pyrithione can be beneficial in the treatment of acne.
- Fungal Infections: It is effective in treating various fungal skin infections due to its antifungal properties.
References
- Warshaw, E. M., et al. (2005). Efficacy of Zinc Pyrithione in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. Dermatology.
- Pierard-Franchimont, C., et al. (2002). Antidandruff shampoo efficacy in dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Scheman, A., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Pyrithione. American Journal of Infection Control.
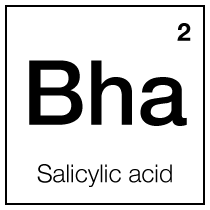
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, Salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
Managing Dermatological Conditions
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove the thickened skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with keratosis pilaris.
References
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.




SHIPPING
- Shipping Guarantee: Guiding you to healthy skin isn’t only about our products; it's also about getting them to you as swiftly as the science behind them. That's why Dermal Health offers a shipping guarantee you can rely on.
- Where We Ship From: Orders are dispatched from our facilities in Pretoria.
- Who We Ship With: We trust only well-known, popular, and dependable courier services with your packages.
- When You'll Get It: Expect confident skin soon! Shipping addresses in Pretoria and Johannesburg will enjoy delivery from same-day to 2 business days. Shipping addresses further from Pretoria may expect delivery within 1-4 business days, depending on the service you select during checkout. Your estimated delivery date will reflect during checkout so that you can mark your calendar.
- Tracking Your Order: Eager to start your DermExcel journey? We don't blame you! You'll receive a tracking number after you place your order so that you can follow your package.
For any shipping inquiries, our customer service team is ready to assist.
RETURNS
180-Day Satisfaction Guarantee
Want to log a return? We’ve got you.
You’re welcome to return any product within 180 days of purchase—even if it’s not defective—as long as it’s sealed, unused, in its original packaging, and still within six months of its labeled expiration date (located on the bottom of the product). We get it: sometimes things change.
For non-defective returns, courier costs will be your responsibility.
If you believe a product is defective, please provide a brief explanation so our team can properly assess and process your claim.
Just complete our quick Return Form and we’ll take it from there.
Healthy Skin Isn’t Complicated. Neither Is Our Return Policy.
Visit our Return Policy page or contact our friendly support team if you need assistance.
SECURE PAYMENT
Dermal Health Science 30-Day Confidence Guarantee: We are passionate about guiding you to healthy skin through medical science. We believe in the quality and effectiveness of our products so much that we offer a 30-Day Confidence Guarantee. If you're unsatisfied with your purchase, simply return it within 30 days for a full refund.
Healthy Skin Is Not Complicated and neither is our return policy. Please visit our detailed return policy or contact our friendly customer service team for more information.
Feel as confident in us as we want you to feel in your skin.
Free Gift with Follicure:

Mini Silicone Scalp Massager
- Dandruff: Formulated to address dandruff, Follicure helps reduce flaking and itchiness on the scalp with its effective antifungal and exfoliating properties.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione and Salicylic acid work synergistically to control inflammation and minimize the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp and body, including redness, scaling, and itchiness.
- Itchy and Irritated Scalp: With its anti-inflammatory and soothing properties, Follicure provides relief from itchiness and irritation, making it an excellent option for calming sensitive or reactive scalp conditions.
- Inflammation: Zinc Pyrithione offers anti-inflammatory benefits that help reduce redness and irritation on both the scalp and body, supporting a calmer, healthier skin barrier.
- Acne and Body Acne (including fungal-related): Follicure’s antibacterial and antifungal ingredients work to treat and prevent acne and body acne, including cases related to yeast or fungal infections, by controlling excess oil and reducing bacterial growth.
- Shaving Bumps / Folliculitis: This formulation helps alleviate folliculitis and shaving-related irritation by clearing pores, reducing inflammation, and targeting bacteria that can lead to bumps.
- Psoriasis: Zinc Pyrithione's anti-inflammatory and antifungal properties make it a supportive choice for managing the redness, scaling, and discomfort often associated with psoriasis.
- Keratosis Pilaris: The exfoliating effect of Salicylic acid helps smooth rough, bumpy skin caused by keratosis pilaris, while Zinc Pyrithione’s anti-inflammatory benefits work to soothe and calm the affected areas.
- Active Scalp Treatment: Apply Follicure 2 to 3 times per week, depending on the severity of your condition. As your symptoms improve, you may reduce the frequency of use.
- Healthy Scalp Maintenance: Apply Follicure to affected or previously affected areas at least once weekly.
- Active Body Treatment: Apply Follicure 1 to 2 times per day, depending on the severity of your condition. As your symptoms improve, reduce the frequency of use to once a day.
scalp treatment
Apply to wet hair and scalp
- Wet hair allows the product to distribute evenly and work effectively on the scalp.
- Take a sufficient amount of Follicure and gently massage it onto the wet scalp, ensuring complete coverage.
- Pay particular attention to areas with visible signs of dandruff, itchiness, or irritation.
- Use the fingertips or the included scalp massager to massage Follicure into the scalp with circular motions. This helps to activate the ingredients and promotes better penetration.
- Leave Follicure on the scalp for approximately 5 to 10 minutes to allow the active ingredients to work effectively.
- After the designated time, thoroughly rinse hair and scalp with lukewarm water, ensuring that all residue is removed.
- It is important to rinse thoroughly, as any remaining product on the scalp may cause irritation or reduce the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Apply Follicure 2 to 3 times per week, depending on the severity of your condition. As your symptoms improve, you may reduce the frequency of use.
- To ensure healthy skin maintenance, apply Follicure to affected areas at least once per week.
body treatment
- Take a sufficient amount of Follicure and apply it to affected areas, focus on areas with visible signs.
- Use your fingertips to gently massage Follicure into the skin with circular motions. This helps activate the ingredients and promotes deeper penetration into the pores.
- Leave Follicure on the skin for approximately 5 to 10 minutes, allowing the active ingredients to work effectively.
- After the designated time, rinse the skin thoroughly with lukewarm water, making sure all product residue is removed.
- Proper rinsing is essential, as any remaining product may cause irritation or reduce the treatment’s effectiveness.
- Apply Follicure in the morning and/or evening, depending on the severity of your symptoms. As your skin improves, you may reduce the frequency to once daily or less.
Active ingredients
- Antifungal Activity: It is effective against a range of fungi, including those that cause dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Zinc Pyrithione inhibits the division of fungal cells, reducing their proliferation.
- Antibacterial Properties: This compound also exhibits antibacterial activity, making it useful in treating and preventing bacterial skin infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Zinc Pyrithione can reduce inflammation, which is beneficial in alleviating symptoms of various inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps in regulating sebum production, which can be beneficial for oily skin and conditions like acne.
- Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Zinc Pyrithione is a common ingredient in anti-dandruff shampoos and is effective in controlling the flaking and itching associated with these conditions.
- Psoriasis: It can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis, particularly in reducing scaling and redness.
- Acne: Due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, Zinc Pyrithione can be beneficial in the treatment of acne.
- Fungal Infections: It is effective in treating various fungal skin infections due to its antifungal properties.
- Warshaw, E. M., et al. (2005). Efficacy of Zinc Pyrithione in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. Dermatology.
- Pierard-Franchimont, C., et al. (2002). Antidandruff shampoo efficacy in dandruff/seborrhoeic dermatitis. International Journal of Cosmetic Science.
- Scheman, A., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Pyrithione. American Journal of Infection Control.
- Keratolytic Action: Salicylic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin by dissolving the intercellular 'glue' that holds skin cells together, helping to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Comedolytic Effect: It is particularly effective in reducing comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by unclogging pores and preventing the formation of new comedones.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Salicylic acid reduces inflammation, which is beneficial in treating acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Sebum Regulation: It helps to regulate oil production, making it a valuable ingredient for managing oily and acne-prone skin.
- Penetration Enhancement: Due to its lipophilic nature, it can penetrate sebum-filled follicles, effectively treating acne located deep within the pores.
- Acne Vulgaris: Salicylic acid is a cornerstone in acne treatment, effectively preventing and treating existing acne lesions.
- Psoriasis: Its keratolytic properties make it helpful in softening and removing scales associated with psoriasis.
- Warts: Salicylic acid is commonly used to treat warts because it can exfoliate and remove the thickened skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: It helps manage seborrheic dermatitis by reducing scaling and redness.
- Keratosis Pilaris: Salicylic acid can aid in smoothing the rough bumps associated with keratosis pilaris.
- Zaenglein, A. L., Pathy, A. L., Schlosser, B. J., Alikhan, A., Baldwin, H. E., Berson, D. S., & Thiboutot, D. M. (2016). Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 74(5), 945-973.e33.
- Kornhauser, A., Coelho, S. G., & Hearing, V. J. (2010). Applications of hydroxy acids: classification, mechanisms, and photoactivity. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 3, 135.
- Zander, E., & Weisman, S. (1992). Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics.
- Gupta, A. K., & Nicol, K. (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione, a compound with potent antifungal and antibacterial properties, has established itself as a cornerstone in the treatment of various skin conditions, particularly those involving Malassezia yeast. Its effectiveness against seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, which are often associated with an overgrowth of Malassezia species, makes it a key ingredient for many dermatological conditions.
Zinc pyrithione’s mode of action is multifaceted, primarily targeting the membrane of fungi and bacteria, thereby disrupting their growth and replication. One of its significant mechanisms involves inhibiting fungal cell membrane transport by blocking the energy production pathway, which is crucial for cell survival.
In Malassezia, yeast, a natural inhabitant of the skin flora, can overgrow and cause conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff; zinc pyrithione's antifungal action is particularly beneficial. It reduces the yeast population on the skin, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with its overgrowth, such as flaking, irritation, and redness.
Its efficacy in treating seborrheic dermatitis is attributed to its ability to reduce the Malassezia count, diminish inflammatory responses, and soothe the skin. Similarly, in dandruff, which is often linked to an excess of Malassezia, zinc pyrithione effectively reduces flaking and itchiness, promoting a healthier scalp environment.
The efficacy of zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is well-documented. Its safety profile and efficacy have been confirmed by numerous studies, with significant improvements observed in both scalp and skin conditions following regular use.
Physiological Effects
Managing Dermatological Conditions
References
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid, a renowned beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is a cornerstone in dermatology and skincare due to its exceptional keratolytic and comedolytic properties. Its unique ability to penetrate oil-laden hair follicle pores makes it particularly effective in treating acne-prone and oily skin types.
Salicylic acid dissolves skin debris (sebum and dead skin cells) that clogs pores and causes acne. It's a mild antibacterial and powerful anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce the redness and swelling associated with breakouts.
What sets salicylic acid apart in dermatological treatments is its ability to exfoliate the skin, not just on the surface but within the pores themselves. This is due to its oil-soluble nature, which allows it to penetrate deep into the pores and dissolve the keratin plugs that lead to blackheads and whiteheads.
Furthermore, salicylic acid also has the capacity to adjust the pH of the skin, creating an environment less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria. Salicylic acid's efficacy in treating various skin conditions, particularly acne, has been extensively documented in the scientific literature. Studies have consistently shown its ability to reduce acne lesions in terms of count and severity. Additionally, Salicylic acid is highly recommended for its effectiveness in treating other skin conditions, such as psoriasis and dandruff, due to its ability to soften and remove scales and flakes from the skin.
Physiological Effects
Managing Dermatological Conditions
References
Full Ingredient list
Aqua, Polyethylene Glycol, Coco-Glucoside, Cocoamidopropyl Betaine, Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate, Salicylic acid, Zinc Pyrithione, Phenoxyethanol & Ethyl hexyl Glycerin, Acrylates Copolymer, Triethanolamine, Coco-Glucoside & Glyceryl Oleate
Follicure
product benefits

Keratolytic action
Exfoliate dead skin cells that accumulate and become trapped in hair follicles. This leads to the overgrowth of dandruff, which causes Malassezia yeast.

Sebum (oil) regulation
Sebum is an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands on the scalp. When it is overproduced, it contributes to the development of dandruff.

Anti-Inflammatory
Reduces inflammation associated with acne and folliculitis. It helps soothe irritated skin, alleviating redness and discomfort.

Anti-fungal action
Disrupt the cell membrane of the dandruff-causing Malassezia yeast, which inhibits its growth and reduces its ability to colonize the scalp.
Indications for Follicure
Itchy Scalp
Folliculitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Dandruff
follicure
mode of action
Anti-inflammatory
Zinc Pyrithione
- Inflammation on the scalp contributes to itchiness, redness, and irritation, which are common symptoms of dandruff. Zinc Pyrithione reduces inflammation on the scalp, which helps to alleviate these symptoms.
- Zinc Pyrithione positively affects the immune system by balancing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the body. Studies published in the Journal of Dermatological Science indicate that Zinc Pyrithione increases the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines in human skin cells. These cytokines are known to be involved in the immune response and are important for regulating inflammation and promoting healing.
- Studies further indicate that Zinc Pyrithione significantly reduces the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. This action boosts the body's natural defenses against the yeast and reduces the severity of dandruff symptoms.
- Cytokine production is a complex process that involves a delicate balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Too much or too little cytokine production can lead to problems with inflammation and immune function. Zinc Pyrithione contributes to a healthy balance between inflammation and immune function.
- Zinc Pyrithione also has direct anti-inflammatory effects on the skin by reducing the production of certain enzymes that contribute to inflammation.
______
SALICYLIC ACID
- Salicylic acid is known to reduce the production of specific pro-inflammatory mediators in the skin, which are often responsible for redness, swelling, and discomfort on the scalp. By moderating these mediators, Salicylic acid helps to calm inflamed areas, reducing the overall inflammatory response.
- Salicylic acid helps regulate sebum production, aiding in the control of scalp oiliness. By managing excessive oil, which is often a contributing factor to dandruff symptoms and scalp discomfort, Salicylic acid promotes a balanced scalp environment that is less susceptible to inflammation and irritation.
Anti-fungal
ZINC PYRITHIONE
- Zinc Pyrithione has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity: It inhibits and reduces the burden of Dandruff-causing Malassezia on the skin and targets gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and other fungi that cause ringworm, athlete's foot, and jock itch.
- Zinc Pyrithione disrupts iron distribution across the yeast wall and effectively starves the yeast of some of the critical processes important in its respiratory function.
- Zinc Pyrithione disrupts the yeast's cell membrane, preventing it from proliferating and reproducing. Zinc Pyrithione binds to the cell membrane of the yeast and causes damage to its structure, which ultimately leads to cell death.
- Zinc Pyrithione also interferes with the metabolic processes of the yeast. It disrupts the uptake of essential nutrients and alters the scalp's pH balance, making it more difficult for the yeast to survive and grow.
- Zinc Pyrithione penetrates the hair follicle where Malassezia resides and has a unique slow-release ability. It persists in the top layer of skin even after rinsing off the product. Therefore, it imparts long-lasting control and sustained release of anti-yeast coverage and suppression of Malassezia yeast overgrowth.
- Yeast, fungi, and bacteria do not develop resistance to Zinc Pyrithione. Consistent application of Zinc Pyrithione results in continuous antimicrobial activity.
Remove dead skin
SALICYLIC ACID
- Salicylic acid exfoliates dead skin cells from the scalp's surface, reducing flakes and dandruff buildup.
- Dandruff is often caused by an accumulation of dead skin cells on the scalp. These cells can become trapped in hair follicles and create an environment favorable for Malassezia's growth. This fungus is associated with dandruff.
- Salicylic acid helps break down the bonds between dead skin cells, making it easier to remove them from the scalp. This helps reduce the buildup on the scalp, which in turn can reduce the amount of dandruff.
- Salicylic acid also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to soothe an irritated scalp and reduce itching and flaking. By reducing inflammation and promoting healthy skin renewal, Salicylic acid helps create an environment less conducive to Malassezia's growth.
- Overall, Salicylic acid is an effective treatment for dandruff because it helps to exfoliate dead skin cells, reduce inflammation, and promote healthy skin renewal.
Body Breakouts & Keratosis Pilaris
ZINC PYRITHIONE
- Reduces the presence of Malassezia yeast and other skin microbes, which contribute to fungal acne and body breakouts. Zinc Pyrithione disrupts fungal and bacterial cell membranes, preventing their growth and spread on areas prone to these issues, such as the back, chest, and shoulders.
- Modulates inflammatory responses by balancing pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which helps to reduce redness, irritation, and discomfort. This action contributes to a calmer skin environment, decreasing the likelihood of flare-ups associated with body acne and keratosis pilaris.
- Reduces microbial buildup by inhibiting the growth of Malassezia yeast and bacteria, contributing to a balanced skin microbiome and reducing the risk of new lesion formation.
______
SALICYLIC ACID
- Provides deep-pore exfoliation by penetrating oil-filled follicles to dissolve trapped dead skin cells and reduce clogging, which helps clear pores and prevent the formation of body breakouts.
- Acts as an effective keratolytic agent by removing excess keratin buildup that leads to rough, bumpy skin texture in keratosis pilaris. Regular use smooths and softens the skin by reducing keratin plugs that can block hair follicles.
clinical data
These clinical trials and studies provide evidence for the efficacy of Salicylic acid in managing dandruff, itchy scalp, and seborrheic dermatitis. Salicylic acid's keratolytic properties enable it to break down dead skin cells, exfoliate the scalp, and reduce flaking and itching, making it a valuable treatment option for these common scalp conditions.
- Squire, R. A., & Goode, K. (1984). A randomised, single-blind, single-centre clinical trial to evaluate comparative clinical efficacy of shampoos containing ciclopirox olamine (1.5%) and salicylic acid (3%), piroctone olamine (1%) and salicylic acid (3%) and zinc pyrithione (1%) and salicylic acid (3%) for the treatment of moderate dandruff. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 5(2), 73-77.
This clinical trial compares the efficacy of shampoos containing salicylic acid in combination with different active ingredients, including ciclopirox olamine, piroctone olamine, and zinc pyrithione. The results indicate that all combinations effectively reduce dandruff symptoms. - Arif, T. (2015). Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 8, 455-461. This comprehensive review outlines the various dermatological applications of salicylic acid, including its use in treating dandruff and other scalp conditions.
The review emphasizes salicylic acid's keratolytic properties, which help to break down the skin's outer layer and reduce flaking and itching. - Garnacho-Saucedo, G., Salido-Vallejo, R., Moreno-Giménez, J. C., Vélez, A., & Campos-Domínguez, M. (2012). Comparative, open-label, randomized, 6-month trial to assess the efficacy and safety of a 1% zinc pyrithione and 1% salicylic acid shampoo vs. 2% ketoconazole shampoo in the treatment of moderate to severe dandruff. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 23(5), 362-366.
This randomized trial compares the efficacy and safety of a 1% zinc pyrithione and 1% salicylic acid shampoo with a 2% ketoconazole shampoo in treating moderate to severe dandruff. The study shows that the combination of zinc pyrithione and salicylic acid provides effective and safe treatment for these conditions. - Ranganathan, S., & Mukhopadhyay, T. (2010). Dandruff: The most commercially exploited skin disease. Indian Journal of Dermatology, 55(2), 130-134.
This review article discusses various treatments for dandruff, including salicylic acid. The authors emphasize that salicylic acid acts as an exfoliant and helps to remove scales and flakes, effectively managing dandruff and associated symptoms.
Testimonials
Renewal Facial Cleanser
I have loved your facial cleanser for a few years now. It really works better than any other product I have used in the past. I have been getting alot of breakouts on my chin these past 6 months. I have tried everything but nothing takes it away
I am genuinely in awe of The Renewal Facial Cleanser. From the very first use, my skin felt cleaner, softer, and more balanced — and with continued use, I can truly see a difference in my skin’s texture and overall glow.
It cleanses thoroughly without stripping my skin or leaving it feeling tight or dry, which is something I’ve always struggled to find in a cleanser. My skin feels refreshed, healthy, and cared for after every wash.
I can confidently say I’ve found the perfect facial cleanser for me and my skin. I won’t be using any other cleanser going forward — this one has earned a permanent place in my skincare routine.
Perfect